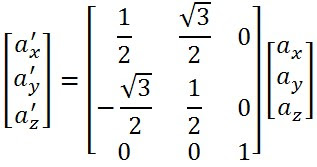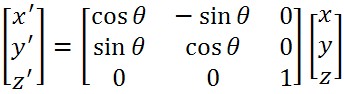Window A is a pane of glass 4 millimeters thick, as shown above. Window B is a sandwich consisting of two extremely thin layers of glass separates by an air gap 2 millimeters thick, as shown above. If the thermal conductivities of glass and air are 0.8 watt/meter Window A is a pane of glass 4 millimeters thick, as shown above. Window B is a sandwich consisting of two extremely thin layers of glass separated by an air gap 2 millimeters thick, as shown above. If the thermal conductivities of glass and air are 0.8 watt/meter oC and 0.025 watt/meter oC, respectively, then the ratio of the heat flow through window A to the heat flow through window B is.
A. 2
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
E. 32
(GR9677 #75)
Solution:
The thicker the glass, the harder for heat to flow → q ∼ 1/t
Thermal conductivity, κ: property of material that allows the flow of heat through the material.
Higher κ → higher the flow of heat → q ∼ κ
qA / qB = (κA / dA )( dB / κB) = (0.8 / 4)(2 /0.025) = 16
Answer: D
Note:
Fourier's Law of Heat Conduction: q = − κ ∇T = − κ dT/dx
q = − κ dT/dx (in 1-D),
T = temperature,
dx = length or thickness, t
q ∼ κ/t
Higher κ → higher the flow of heat → q ∼ κ
qA / qB = (κA / dA )( dB / κB) = (0.8 / 4)(2 /0.025) = 16
Answer: D
Note:
Fourier's Law of Heat Conduction: q = − κ ∇T = − κ dT/dx
q = − κ dT/dx (in 1-D),
T = temperature,
dx = length or thickness, t
q ∼ κ/t