
A beam of light has a small wavelength spread δλ about a central wavelength λ. The beam travels in vacuum until it enters a glass plate at an angle θ relative to the normal to the plate. The index of refraction of the glass is given by n(λ). The angular spread δθ' is given by
A.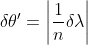
B.}{n}\delta\lambda&space;\right&space;|)
C.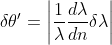
D.
E.}{d\lambda}&space;\delta&space;\lambda\right&space;|)
Snell's Law: n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2
Given:
n1 = 1 for vacuum
n2 = n(λ)
θ1 = θ
θ2 = θ'
sin θ = n(λ) sin θ'
Take the derivative of the equation with respect to λ:
dsin θ/dλ = dn(λ)sin θ'/dλ ...(Eq.1)
θ is a constant → dsin θ/dλ = 0
Eq.1 →
0 = dn(λ)sin θ'/dλ
0 = n(λ) (dsin θ'/dλ) + sin θ' (dn(λ)/dλ) ...(Eq.2)
Since n is a function of λ, θ' is also a function λ →
dsin θ'/dλ = (dsin θ'/dθ')(dθ'/dλ) = cos θ' (dθ'/dλ)
Eq.2 →
0 = n(λ) cos θ' (dθ'/dλ) + sin θ' (dn(λ)/dλ)
n(λ) cos θ' (dθ'/dλ) = − sin θ' (dn(λ)/dλ)
n(λ) (dθ'/dλ) = − tan θ' (dn(λ)/dλ)
dθ'/dλ = − (tan θ'/n(λ)) (dn(λ)/dλ)
δθ' = |(tan θ'/n(λ)) (dn(λ)/dλ)|
Answer: E
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
(GR0177 #97)
Solution:Snell's Law: n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2
Given:
n1 = 1 for vacuum
n2 = n(λ)
θ1 = θ
θ2 = θ'
sin θ = n(λ) sin θ'
Take the derivative of the equation with respect to λ:
dsin θ/dλ = dn(λ)sin θ'/dλ ...(Eq.1)
θ is a constant → dsin θ/dλ = 0
Eq.1 →
0 = dn(λ)sin θ'/dλ
0 = n(λ) (dsin θ'/dλ) + sin θ' (dn(λ)/dλ) ...(Eq.2)
Since n is a function of λ, θ' is also a function λ →
dsin θ'/dλ = (dsin θ'/dθ')(dθ'/dλ) = cos θ' (dθ'/dλ)
Eq.2 →
0 = n(λ) cos θ' (dθ'/dλ) + sin θ' (dn(λ)/dλ)
n(λ) cos θ' (dθ'/dλ) = − sin θ' (dn(λ)/dλ)
n(λ) (dθ'/dλ) = − tan θ' (dn(λ)/dλ)
dθ'/dλ = − (tan θ'/n(λ)) (dn(λ)/dλ)
δθ' = |(tan θ'/n(λ)) (dn(λ)/dλ)|
Answer: E
No comments :
Post a Comment